We perform nearly all of our daily tasks with the hand, making Arm Muscle Injuries vital component of our body. Without it, we cannot do a single work, not even our basic activity. Although hands are important in our lives, we may unintentionally harm them at times, possibly due to an accident or irregular exercise. People who exercise with weights, are athletes, are runners, are construction workers, or spend a lot of time in front of a computer are particularly susceptible to this issue. We frequently dismiss pain as normal, but if left untreated, a minor muscle injury can develop into more serious issues down the road. As a result, it is critical to understand hand muscle injuries and take the appropriate action. However, hand muscles can occasionally be injured as a result of accidents, improper exercise, or overwork. Arm muscular Injury is the name given to this kind of muscular injury. It can range in severity from minor discomfort to severe tears. Arm muscle injuries distract our work, even sedentary work.
Table of Contents
Arm muscle injury symptoms
There are various kinds of arm muscle injuries, including strains, tears, and soreness and swelling. As a result, the symptoms may also differ. Arm muscle injury symptoms are explored based on percussion. The typical signs of arm muscle damage are listed below:
Pain: The most prevalent and early sign of a hand muscle injury is pain. Immediately following the injury, the pain may begin abruptly and intensely, or it may progressively worsen over time. Attempting to move the muscle or excessive force may exacerbate the pain. In many situations, the pain is localized, while in others, it radiates to nearby muscles. Sometimes we reckon pain is normal, but it may be the initial symptom of any serious injury. Arm muscle injury symptoms begin with pain and then spread.
Swelling: Fluid buildup may cause the wounded area to swell. When inflammation builds up inside the muscle, this swelling happens. This swelling makes it challenging to straighten or bend the arm, and the afflicted area may occasionally feel heated.
Bruising or Discoloration: Among various arm muscle injury symptoms, bruising is the most common symptom. Blood frequently pools beneath the skin of the injured arm muscle, resulting in a reddish, bluish, or purple discoloration. Blood pools beneath the skin as a result of tiny blood capillaries inside the muscle rupturing, giving this coloring. Typically, this discoloration begins a day after the injury occurs, develops slowly, and changes color from blue to green, then yellow, before finally fading away.
Tenderness
Typically, this kind of discomfort is restricted to a single location. It is frequently characterized as a sharp pain or deep ache. A significant muscular rupture may be excruciating to the touch, whereas slight damage may provide modest discomfort. The severity of the pain depends on the type of injury. In order to identify the best area for treatment, tenderness is a sign that tendons or muscle fibers are injured. This symptom is frequently used by doctors to aid in the diagnosis of illnesses like
· The location of the injury
· Finding a particular injured muscle
· Identifying any bleeding or swelling
If the tenderness does not go away in a few days or worsens, it may be caused by a deep muscle issue or internal bleeding. You should get medical help right away in this situation and not put it off.
Restricted Range of Motion
Lifting, turning, or folding the arm requires strength or difficulty. Often, discomfort and swelling hinder regular use of the arm. Moreover, it can be challenging to do even basic things like holding anything, combing hair, or getting dressed.
Muscle Tightness or Spasm
When a hand muscle is injured, it frequently feels taut or trembles. We refer to this as muscle spasm or muscle tightness. A muscle that is suddenly too tight to extend or contract normally is said to have this condition. The sensation is quite uncomfortable and painful. This disorder causes the muscle to become rigid. Patients frequently complain that a certain hand portion is “frozen” or rigid. There are moments when the tightness is so bad that moving your hand makes it hurt even more. This spasm may come on quickly, particularly while you’re sleeping or have just woken up.
Typical reasons for this issue include:
· Stress on muscles as a result of injury or overwork
· Dehydration, or not drinking enough water
· The body’s lack of certain minerals, such as potassium and magnesium
· Keeping your hands still for an extended period of time
· In frigid conditions, muscles can readily constrict and cramp.
Treatment for Arm Muscle Injuries
Mild, moderate, and severe arm muscle injuries are all possible. As a result, how they are treated also depends on the kind of injury. In extreme circumstances, specific therapy or surgery under a doctor’s supervision may be necessary, but in other cases, simple home treatment is sufficient.
A detailed treatment plan for arm muscle injuries is provided below:
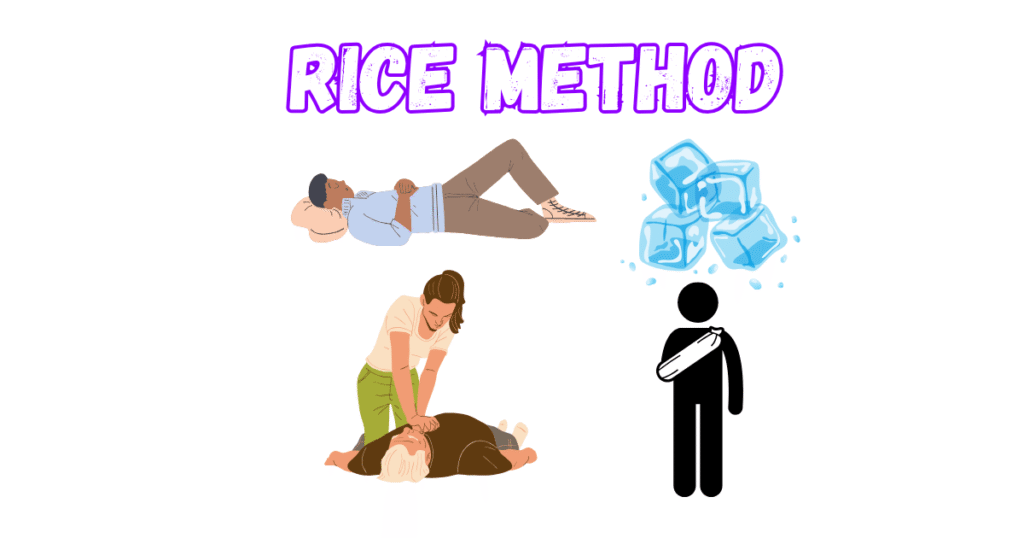
First Aid (RICE Method)
R = Rest: Provide total rest to the afflicted muscle. Steer clear of pressure and weight bearing to prevent further muscle damage.
I = Ice: Every two to three hours, apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes. This controls blood circulation and reduces pain and edema.
C = Compression: Apply a thin elastic bandage to the afflicted area. However, do not wrap it too tightly to avoid blocking blood flow.
E = Elevation: Maintain the arm above the heart. This reduces edema.
Medication
The second phase of treatment for arm muscle injuries is medication, while the first phase of treatment is the most important. There are a plethora of approaches for medication; among these, the most common medicines are well known for use for arm muscle injury.
As directed by the physician, the following kinds of drugs are typically used to treat pain or swelling:
· Pain relievers: Ibuprofen or paracetamol
· Anti-inflammatory medications
· Gels or ointments (like Diclofenac gel)
Physiotherapy
Treatment under the supervision of a qualified physiotherapist is required if the muscle injury does not recover in a few days. Therapy consists of:
· Simple motion and stretching exercises
· Ultrasound treatment
· Therapy using hot or cold packs
· When required, electrotherapy
· Through physiotherapy, the muscles’ natural structure, strength, and flexibility can be restored.
Surgery
The physician uses specialized tools to repair the torn muscle or tissue or sews it back together. Tissue transplants are occasionally utilized to rebuild the tendon or muscle. In the event that the nerve is damaged, microsurgery is used to heal it.
FAQ
1. Can an injury to a muscle repair itself?
Although they can cause discomfort and make daily tasks more difficult, muscle strains usually go away on their own.
2. How much time does it take for muscles to heal?
It typically takes 42 to 72 hours for your muscle fibers to recuperate, depending on your workout and the actions you do thereafter.
3. What is the best food for recovering muscles?
Protein: Amino acids found in protein aid in the body’s muscle tissue growth and repair. Foods derived from animals, such as cheese, fish, poultry, and cattle, are excellent sources of protein.
Learn More
1 thought on “A Guide to Preventing Arm Muscle Injuries”